Python数据分析-看了这篇文章,数据清洗你也就完全掌握了
所有做数据分析的前提就是:你得有数据,而且已经经过清洗,整理成需要的格式。
不管你从哪里获取了数据,你都需要认真仔细观察你的数据,对不合规的数据进行清理,虽然不是说一定要有这个步骤,但是这是一个好习惯,因为保不齐后面分析的时候发现之前因为没有对数据进行整理,而导致统计的数据有问题,今天小编就把平时用的数据清洗的技巧进行一个梳理,里面可能很多你都懂,那就当温习了吧!
文章大纲:
- 如何更有效的导入你的数据
- 全面的观察数据
- 设置索引
- 设置标签
- 处理缺失值
- 删除重复项
- 数据类型转换
- 筛选数据
- 数据排序
- 处理文本
- 合并&匹配
导入数据:
- pd.read_excel("aa.xlsx")
- pd.read_csv("aa.xlsx")
- pd.read_clipboard
如何有效的导入数据:
1、限定导入的行,如果数据很大,初期只是为了查看数据,可以先导入一小部分:
- pd.read_csv("aaa.csv",nrows=1000)
- pd.read_excel("aa.xlsx",nrows=1000)
2、如果你知道需要那些列,而且知道标签名,可以只导入需要的数据:
- pd.read_csv("aaa.csv",usecols=["A","B"])
- pd.read_excel("aa.xlsx",usecols=["A","B"])
3、关于列标签,如果没有,或者需要重新设定:
- pd.read_excel("aa.xlsx",header=None)#不需要原来的索引,会默认分配索引:0,1,2
- pd.read_excel("aa.xlsx",header=1)#设置第二行为列标签
- pd.read_excel("aa.xlsx",header=[1,2])#多级索引
- pd.read_csv("aaa.csv",header=None)
- pd.read_csv("aaa.csv",header=1)
- pd.read_csv("aaa.csv",header=[1,2])
4、设置索引列,如果你可以提供一个更有利于数据分析的索引列,否则分配默认的0,1,2:
- pd.read_csv("aaa.csv",index_col=1)
- pd.read_excel("aa.xlsx",index_col=2)
5、设置数值类型,这一步很重要,涉及到后期数据计算,也可以后期设置:
- pd.read_csv("aaa.csv",converters = {'排名': str, '场次': float})
- data = pd.read_excel(io, sheet_name = 'converters', converters = {'排名': str, '场次': float})
全面的查看数据:
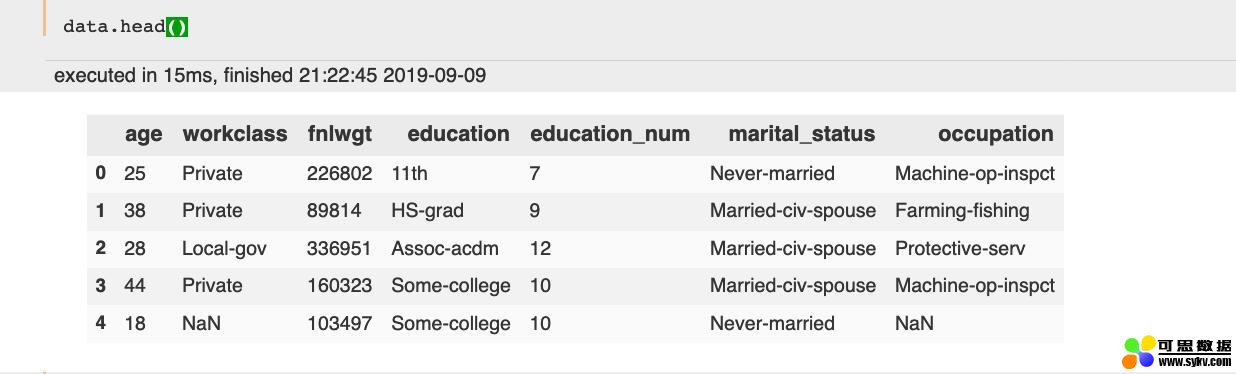
查看前几行:
- data.head()
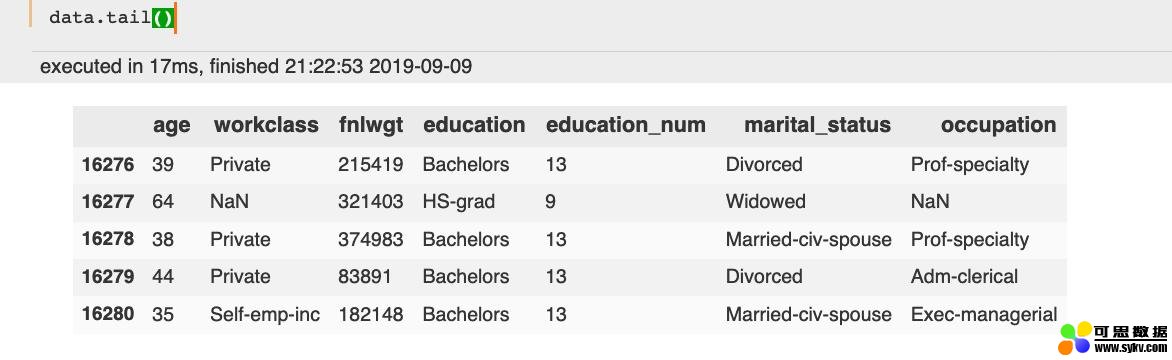
查看末尾几行:
查看数据维度:
- data.shape(16281, 7)
查看DataFrame的数据类型
- df.dtypes
查看DataFrame的索引
- df.index
查看DataFrame的列索引
- df.columns
查看DataFrame的值
- df.values
查看DataFrame的描述
- df.describe()
某一列格式:
- df['B'].dtype
设置索引和标签:
有时我们经常需要重新设置索引列,或者需要重新设置列标签名字:
重新设置列标签名:
- df.rename(columns={"A": "a", "B": "c"})
- df.rename(index={0: "x", 1: "y", 2: "z"})
重新设置索引:
- df.set_index('month')
重新修改行列范围:
- df.reindex(['http_status', 'user_agent'], axis="columns")
- new_index= ['Safari', 'Iceweasel', 'Comodo Dragon', 'IE10', 'Chrome']
- df.reindex(new_index)
取消原有索引:
- df.reset_index()
处理缺失值和重复项:
判断是否有NA:df.isnull().any()
填充NA:
- pf.fillna(0)
删除含有NA的行:
- rs=df.dropna(axis=0)
删除含有NA的列:
- rs=df.dropna(axis=1)
删除某列的重复值:
- a= frame.drop_duplicates(subset=['pop'],keep='last')
数据类型转换:
df.dtypes:查看数值类型
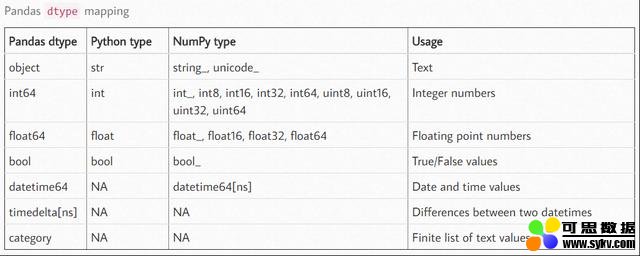
- astype()强制转化数据类型
- 通过创建自定义的函数进行数据转化
- pandas提供的to_nueric()以及to_datetime()
- df["Active"].astype("bool")
- df['2016'].astype('float')
- df["2016"].apply(lambda x: x.replace(",","").replace("$","")).astype("float64")
- df["Percent Growth"].apply(lambda x: x.replace("%","")).astype("float")/100
- pd.to_numeric(df["Jan Units"],errors='coerce').fillna(0)
- pd.to_datetime(df[['Month', 'Day', 'Year']])
筛选数据:
1、按索引提取单行的数值
- df_inner.loc[3]
2、按索引提取区域行数值
- df_inner.iloc[0:5]
3、提取4日之前的所有数据
- df_inner[:’2013-01-04’]
4、使用iloc按位置区域提取数据
- df_inner.iloc[:3,:2] #冒号前后的数字不再是索引的标签名称,而是数据所在的位置,从0开始,前三行,前两列。
5、适应iloc按位置单独提起数据
- df_inner.iloc[[0,2,5],[4,5]] #提取第0、2、5行,4、5列
6、使用ix按索引标签和位置混合提取数据
- df_inner.ix[:’2013-01-03’,:4] #2013-01-03号之前,前四列数据
7、使用loc提取行和列
- df_inner.loc(2:10,"A":"Z")
8、判断city列里是否包含beijing和shanghai,然后将符合条件的数据提取出来
- df_inner[‘city’].isin([‘beijing’])
- df_inner.loc[df_inner[‘city’].isin([‘beijing’,’shanghai’])]
9、提取前三个字符,并生成数据表
- pd.DataFrame(category.str[:3])
10、使用“与”进行筛选
- df_inner.loc[(df_inner[‘age’] > 25) & (df_inner[‘city’] == ‘beijing’), [‘id’,’city’,’age’,’category’,’gender’]]
11、使用“或”进行筛选
- df_inner.loc[(df_inner[‘age’] > 25) | (df_inner[‘city’] == ‘beijing’), [‘id’,’city’,’age’,’category’,’gender’]].sort([‘age’])
12、使用“非”条件进行筛选
- df_inner.loc[(df_inner[‘city’] != ‘beijing’), [‘id’,’city’,’age’,’category’,’gender’]].sort([‘id’])
13、对筛选后的数据按city列进行计数
- df_inner.loc[(df_inner[‘city’] != ‘beijing’), [‘id’,’city’,’age’,’category’,’gender’]].sort([‘id’]).city.count()
14、使用query函数进行筛选
- df_inner.query(‘city == [“beijing”, “shanghai”]’)
15、对筛选后的结果按prince进行求和
- df_inner.query(‘city == [“beijing”, “shanghai”]’).price.sum()
数据排序
按照特定列的值排序:
- df_inner.sort_values(by=[‘age’])
按照索引列排序:
- df_inner.sort_index()
升序
- df_inner.sort_values(by=[‘age’],ascending=True)
降序
- df_inner.sort_values(by=[‘age’],ascending=False)
合并匹配:
merge
- 1.result = pd.merge(left, right, on='key')
- 2.result = pd.merge(left, right, on=['key1', 'key2'])
- 3.result = pd.merge(left, right, how='left', on=['key1', 'key2'])
- 4.result = pd.merge(left, right, how='right', on=['key1', 'key2'])
- 5.result = pd.merge(left, right, how='outer', on=['key1', 'key2'])
2、append
- 1.result = df1.append(df2)
- 2.result = df1.append(df4)
- 3.result = df1.append([df2, df3])
- 4.result = df1.append(df4, ignore_index=True)
4、join
left.join(right, on=key_or_keys)
- 1.result = left.join(right, on='key')
- 2.result = left.join(right, on=['key1', 'key2'])
- 3.result = left.join(right, on=['key1', 'key2'], how='inner')
5、concat
- 1.result = pd.concat([df1, df4], axis=1)
- 2.result = pd.concat([df1, df4], axis=1, join='inner')
- 3.result = pd.concat([df1, df4], axis=1, join_axes=[df1.index])
- 4.result = pd.concat([df1, df4], ignore_index=True)
文本处理:
1. lower()函数示例
- s = pd.Series(['Tom', 'William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t', np.nan, '1234','SteveMinsu'])
- s.str.lower()
2. upper()函数示例
- s = pd.Series(['Tom', 'William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t', np.nan, '1234','SteveMinsu'])
- s.str.upper()
3. len()计数
- s = pd.Series(['Tom', 'William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t', np.nan, '1234','SteveMinsu'])
- s.str.len()
4. strip()去除空格
- s = pd.Series(['Tom ', ' William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- s.str.strip()
5. split(pattern)切分字符串
- s = pd.Series(['Tom ', ' William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- s.str.split(' ')
6. cat(sep=pattern)合并字符串
- s = pd.Series(['Tom ', ' William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- s.str.cat(sep=' <=> ')
- 执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
- Tom <=> William Rick <=> John <=> Alber@t
7. get_dummies()用sep拆分每个字符串,返回一个虚拟/指示dataFrame
- s = pd.Series(['Tom ', ' William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- s.str.get_dummies()
8. contains()判断字符串中是否包含子串true; pat str或正则表达式
- s = pd.Series(['Tom ', ' William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- s.str.contains(' ')
9. replace(a,b)将值pat替换为值b。
- s = pd.Series(['Tom ', ' William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- .str.replace('@','$')
10. repeat(value)重复每个元素指定的次数
- s = pd.Series(['Tom ', ' William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- s.str.repeat(2)
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
- 0 Tom Tom
- 1 William Rick William Rick
- 2 JohnJohn
- 3 Alber@tAlber@t
11. count(pattern)子串出现次数
- s = pd.Series(['Tom ', ' William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- print ("The number of 'm's in each string:")
- print (s.str.count('m'))
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
The number of 'm's in each string:
- 0 1
- 1 1
- 2 0
- 3 0
12. startswith(pattern)字符串开头是否匹配子串True
- s = pd.Series(['Tom ', ' William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- print ("Strings that start with 'T':")
- print (s.str. startswith ('T'))
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
Strings that start with 'T':
- 0 True
- 1 False
- 2 False
- 3 False
13. endswith(pattern)字符串结尾是否是特定子串 true
- s = pd.Series(['Tom ', ' William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- print ("Strings that end with 't':")
- print (s.str.endswith('t'))
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
Strings that end with 't':
- 0 False
- 1 False
- 2 False
- 3 True
14. find(pattern)查子串首索引,子串包含在[start:end];无返回-1
- s = pd.Series(['Tom ', ' William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- print (s.str.find('e'))
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
- 0 -1
- 1 -1
- 2 -1
- 3 3
注意:-1表示元素中没有这样的模式可用。
15. findall(pattern)查找所有符合正则表达式的字符,以数组形式返回
- s = pd.Series(['Tom ', ' William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- print (s.str.findall('e'))
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
- 0 []
- 1 []
- 2 []
- 3 [e]
空列表([])表示元素中没有这样的模式可用。
16. swapcase()变换字母大小写,大变小,小变大
- s = pd.Series(['Tom', 'William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- s.str.swapcase()
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
- tOM
- wILLIAM rICK
- jOHN
- aLBER
17. islower()检查是否都是大写
- s = pd.Series(['Tom', 'William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- s.str.islower()
18. isupper()检查是否都是大写
- s = pd.Series(['TOM', 'William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- s.str.isupper()
19. isnumeric()检查是否都是数字
- s = pd.Series(['Tom', '1199','William Rick', 'John', 'Alber@t'])
- s.str.isnumeric()

时间:2019-09-12 00:00 来源:可思数据 转发量:次
声明:本站部分作品是由网友自主投稿和发布、编辑整理上传,对此类作品本站仅提供交流平台,转载的目的在于传递更多信息及用于网络分享,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,不为其版权负责。如果您发现网站上有侵犯您的知识产权的作品,请与我们取得联系,我们会及时修改或删除。
相关文章:
- [数据挖掘]底层I/O性能大PK:Python/Java被碾压,Rust有望取代
- [数据挖掘]大数据分析的技术有哪些?
- [数据挖掘]大数据分析会遇到哪些难题?
- [数据挖掘]RedMonk语言排行:Python力压Java,Ruby持续下滑
- [数据挖掘]不得了!Python 又爆出重大 Bug~
- [数据挖掘]TIOBE 1 月榜单:Python年度语言四连冠,C 语言再次
- [数据挖掘]TIOBE12月榜单:Java重回第二,Python有望四连冠年度
- [数据挖掘]这个可能打败Python的编程语言,正在征服科学界
- [数据挖掘]2021年编程语言趋势预测:Python和JavaScript仍火热,
- [数据挖掘]Spark 3.0重磅发布!开发近两年,流、Python、SQL重
相关推荐:
网友评论: